Understanding Meniscus Tears: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Author :
Category :
Published Date : May 06, 2023
Table of Contents
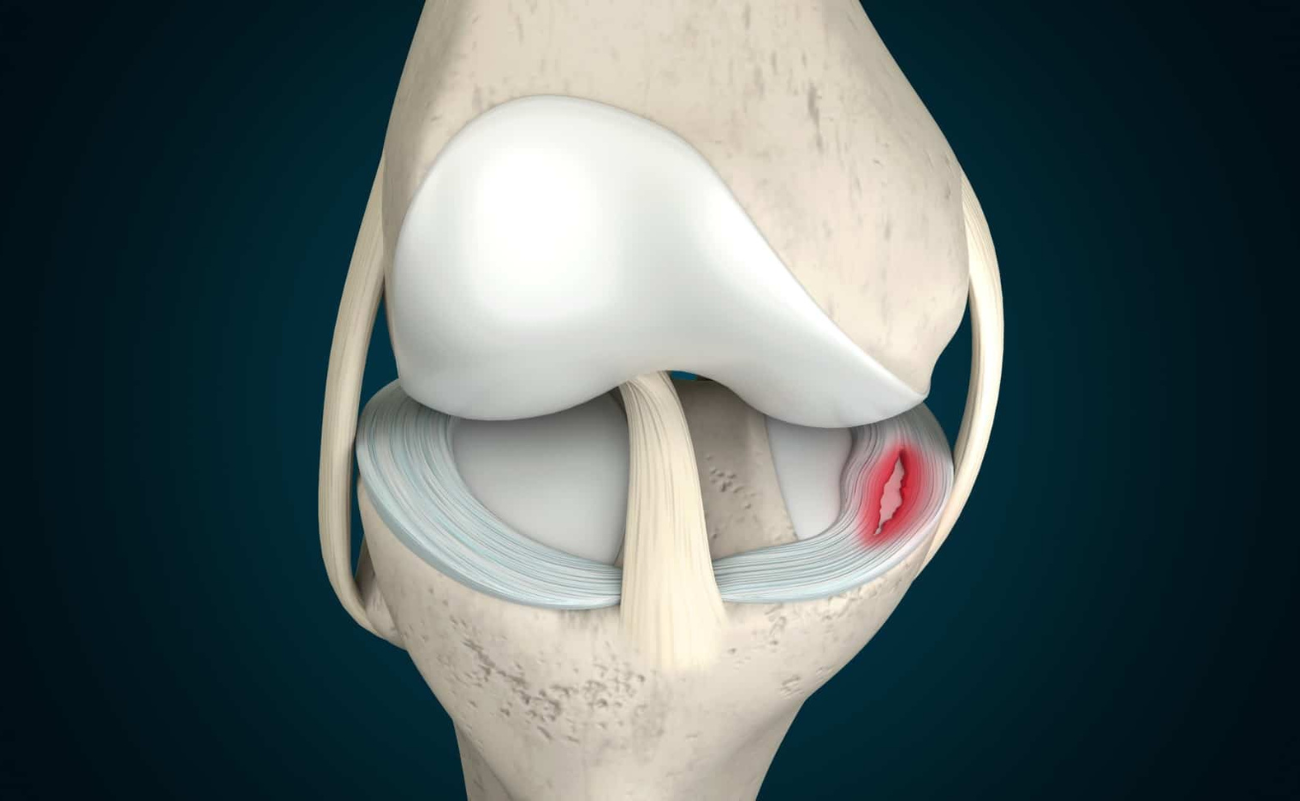
The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage in the knee joint that acts as a cushion between the femur (thighbone) and tibia (shinbone). It plays a crucial role in absorbing shock, providing stability, and facilitating smooth movement of the knee. However, the meniscus can be susceptible to tears, which can cause pain, swelling, and limited mobility. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for meniscus tears.
Anatomy and Function of the Meniscus
To understand meniscus tears, it's essential to grasp the anatomy and function of the meniscus. The knee joint consists of two menisci: the medial meniscus on the inner side of the knee and the lateral meniscus on the outer side. These structures act as shock absorbers, distribute forces across the knee joint, and help with joint stability and lubrication.
Causes of Meniscus Tears
Meniscus tears can occur due to various reasons, including:
Traumatic Injury
A sudden twist or forceful rotation of the knee joint, such as during sports activities or accidents, can cause a meniscus tear. This is commonly seen in athletes who participate in sports involving quick direction changes or pivoting movements.
Degenerative Changes
As we age, the meniscus gradually weakens and becomes more prone to tears. Degenerative tears are often associated with age-related changes, such as reduced blood supply and wear and tear of the cartilage.
Types and Symptoms of Meniscus Tears
Meniscus tears can be classified into different types, including:
Radial Tears
These tears occur from the inside to the outside of the meniscus and are often stable.
Horizontal Tears
These tears are parallel to the tibial plateau and can interfere with knee joint function.
Bucket Handle Tears
These tears cause a portion of the meniscus to dislodge and move into the joint, leading to significant pain and restricted movement.
The symptoms of a meniscus tear can vary depending on the type and severity of the tear. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Pain, particularly along the joint line
- Swelling and stiffness
- Difficulty fully extending or bending the knee
- Clicking or locking sensation
- Limited range of motion
- Instability or giving way of the knee
Diagnosis of Meniscus Tears
When a meniscus tear is suspected, a thorough evaluation is necessary to confirm the diagnosis. This typically involves:
Medical History and Physical Examination
The healthcare provider will ask about symptoms, medical history, and any recent knee injuries. They will also perform a physical examination, which may include specific tests to assess the stability and function of the knee joint.
Imaging Tests
X-rays can help rule out other knee problems, while magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provides detailed images of the meniscus and helps identify the location, size, and severity of the tear.
V. Treatment Options for Meniscus Tears
The treatment approach for meniscus tears depends on several factors, including the type of tear, location, symptoms, and the individual's age and activity level. The main treatment options include:
Conservative Management
- Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE): These measures can help reduce pain and swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Specific exercises can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve stability, and restore range of motion.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Surgical Intervention
Arthroscopic Surgery
In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief or for certain types of meniscus tears, arthroscopic surgery may be recommended. This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a tiny camera (arthroscope) and surgical instruments through small incisions in the knee to repair or remove the torn portion of the meniscus.
During the surgery, the surgeon will carefully evaluate the tear and determine the most appropriate course of action. For minor tears, the damaged area may be trimmed or smoothed out to prevent further irritation. In more severe cases, the torn meniscus may be repaired using sutures or other techniques to promote healing and preserve the structure of the meniscus.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Following meniscus surgery, a comprehensive rehabilitation program is crucial to restore strength, flexibility, and function to the knee. The specific rehabilitation protocol will depend on the extent of the tear, the surgical technique used, and the individual's overall health.
Initially, the focus will be on controlling pain and swelling through ice, elevation, and medications as prescribed by the surgeon. Gradually, physical therapy will be initiated to improve the range of motion, muscle strength, and stability of the knee joint. Therapists will guide patients through exercises and activities tailored to their specific needs and goals.
The recovery period can vary, but most individuals can expect to return to their normal activities within a few weeks to a few months. It's important to follow the rehabilitation program diligently and communicate any concerns or setbacks to the healthcare team.
Prevention and Tips for Meniscus Health
While not all meniscus tears can be prevented, there are steps one can take to reduce the risk of injury and maintain overall knee health:
Strengthen the Muscles
Regular exercise, particularly strengthening exercises for the quadriceps and hamstrings, can help support the knee joint and reduce stress on the meniscus.
Warm-Up and Stretch
Before engaging in physical activities or sports, it's important to warm up properly and perform dynamic stretches to prepare the muscles and joints for movement.
Use Proper Techniques
Whether it's lifting heavy objects, jumping, or pivoting, using proper body mechanics and techniques can help minimize the risk of knee injuries.
Wear Appropriate Footwear
Choose footwear that provides proper support and cushioning, especially when participating in high-impact activities or sports.
Listen to Your Body
Pay attention to any signs of knee pain, discomfort, or instability. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical attention promptly.
Conclusion
Meniscus tears can significantly impact one's quality of life, but with early recognition, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment, individuals can effectively manage this common knee injury. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for meniscus tears empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare and take necessary steps to prevent further damage.
If you experience knee pain or suspect a meniscus tear, consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan. Remember, proper care and timely intervention can contribute to optimal recovery and long-term knee health.
